Agent Call
Agent calls are the defining concept of LLLM. Instead of exposing raw LLM completions, every agent implements a deterministic state machine that must transition from an initial dialog to a well-defined output state (or raise an error). This contract keeps downstream systems simple—no consumer needs to guess whether the model "felt done".
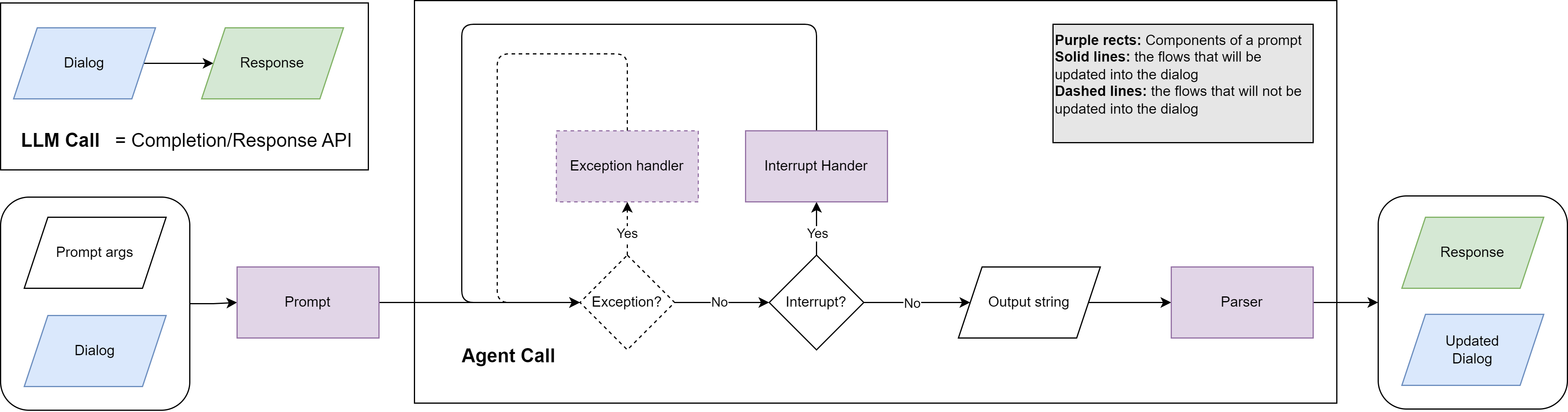
LLM Call vs. Agent Call
| LLM Call | Agent Call | |
|---|---|---|
| Input | Flat list of chat messages. | Dialog seeded with a top-level Prompt, plus optional prompt arguments. |
| Output | Raw model string plus metadata. | Parsed response, updated dialog, and function-call trace. |
| Responsibility | Caller decides whether to retry, parse, or continue. | Agent handles retries, parsing, exception recovery, and interrupts until it reaches the desired state. |
| Determinism | Best-effort. | Guaranteed next state or explicit exception. |
The Agent dataclass in lllm/llm.py exposes call(dialog, extra, args, parser_args) to run the loop. Orchestrator (and AsyncOrchestrator) wrap this call with logging (StreamWrapper) and a user-friendly .call(task) signature for system builders. Under the hood each agent delegates to a provider implementation (lllm.providers.BaseProvider) so the same loop can target OpenAI’s Chat Completions API or the Responses API by toggling the api_type field on the agent configuration.
State Machine Lifecycle
- Seed dialog –
Agent.init_dialogplaces the system prompt (usually pulled fromPROMPT_REGISTRYviaPrompts('agent_root')). - Send invocation prompt – Systems typically
send_messagewith a task-specific prompt (e.g.,prompts('task_query')). TheDialog.top_promptpointer remembers which prompt introduced the latest user turn. - LLM call – The provider decides whether to hit
chat.completionsor the Responses API depending onapi_type(completionvs.response) and prompt needs, attaches registered functions/MCP servers, and sends the dialog history. - Response handling –
- If the model returned tool calls, LLLM invokes each linked
Function, appends a tool message generated byPrompt.interrupt_handler, and loops again. - If the parser raised a
ParseError,Prompt.exception_handleris invoked with the error message and the dialog is retried (up tomax_exception_retry). - Network/runtime issues trigger exponential backoff, optional "LLM recall" retries, and persist structured error reports.
- Completion – As soon as the model returns a valid assistant message without function calls, the loop terminates and the parsed payload plus the final dialog are returned.
Interrupt vs. Exception Handling
Each Prompt can specify inline handlers:
- Exception handler (
Prompt.exception_handler) receives{error_message}whenever parsing or validation fails. These dialog branches are pruned after handling. - Interrupt handler (
Prompt.interrupt_handler) receives{call_results}after function execution. These branches remain in the dialog for transparency, and a final "stop calling functions" prompt ensures the agent produces a natural-language summary.
Handlers inherit the prompt’s parser, XML/MD tags, and allowed functions, so a single definition covers the entire agent loop.
Function Calls, MCP, and Tools
Prompt instances can bundle:
Functionobjects (structured JSON schemas) that wrap Python callables.- MCP server descriptors for OpenAI’s Model Context Protocol tools.
- Optional
allow_web_searchandcomputer_use_confighints that enable OpenAI-native web search or computer-use toolchains when supported by the model card (const.py).
During an agent call, every function call is tracked as a FunctionCall object with arguments, result, result_str, and error_message. The loop prevents duplicate calls by checking FunctionCall.is_repeated.
Selecting the LLM API
Each agent entry in agent_configs accepts api_type:
[agent_configs.researcher]
model_name = "gpt-4o-mini"
system_prompt_path = "research/system"
api_type = "response" # or "completion"
completion(default) uses Chat Completions. IfPrompt.formatis set, the provider automatically switches tobeta.chat.completions.parseso you can keep using Pydantic response formats.responseopts into the OpenAI Responses API. When the target model advertisesweb_searchorcomputer_usefeatures,Prompt.allow_web_searchandPrompt.computer_use_configmaterialize as native OpenAI tools. Responses API tool outputs are surfaced back throughPrompt.interrupt_handlerasRoles.USERmessages so the assistant can summarize the tool transcript.
Implementing Custom Agents
To ship a new agent:
- Subclass
Orchestrator, setagent_typeandagent_group(e.g.,['researcher', 'editor']). - Within
__init__, pick prompts viaPrompts('<root>')and designate which sub-agent handles each task. - Implement
call(self, task, **kwargs)to orchestrate dialogs (seetemplate/example/system/agent/agent.py).
Agents register themselves automatically through Orchestrator.__init_subclass__, so once your class is imported it becomes available to build_agent and the templates.